Dental Caries
The word caries means decay or rottening. It is the most commonly reported oral disease. Decay can begin on any area of a tooth and its appearance can vary from a small blackish spot to a severely destructed and discolored structure depending upon the severity of the disease.
Causes:
- Carbohydrate rich diet
Ex: Chips, French fries


- Sticky foods with excess sugars
Ex: Chocolates (Cadbury, Caramel etc)

- Prolonged acidic environment in oral cavity
Ex: Lack of rinsing oral cavity after any meal

- Oral micro-organisms
Mechanism:
Few strains of oral microbes digest the carbohydrates present in our diet and produce acids which will eat away the mineral part of the tooth structure. The same microbes produce protein digesting enzymes which will destroy the non mineral part of the tooth structure. In course of time it will reach deeper parts of the tooth where nerves exist. Stimulation of these nerve endings will thus cause severe pain.
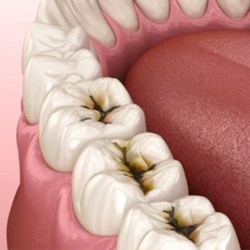
Pit & Fissure Caries
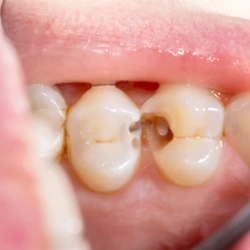
Smooth Surface Caries
Treatment options:
The type of treatment depends on the severity of the disease. If it is very small and is without symptoms like pain, then the damaged portion of the tooth will be removed and will be filled using any dental cement of choice. If it is severe and is causing continuous pain, then the options will be either to undergo root canal treatment or complete tooth extraction depending upon the extent of damage to tooth structure. Both the methods will be done under local anesthesia so that the patient will not have any pain or discomfort.
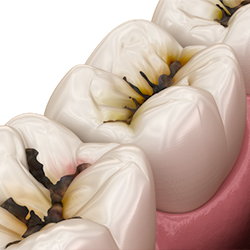
Before
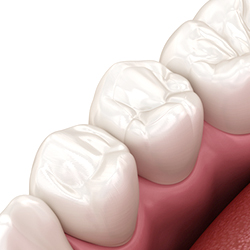
After
Preventive Measures:
Regular visit to a dentist, at least once in 6 months is suggestible. Decay or caries can be prevented at early stages by various methods like pit and fissure sealants, fluoride applications, usage of fluoride tooth pastes and many other methods.
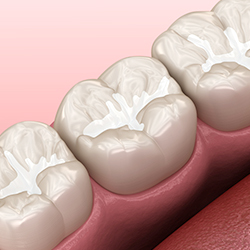
Pit and fissure sealants
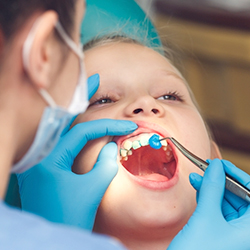
Topical fluoride applications

Fluoridated tooth paste